UAE’s Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) will further launch a number of transformational projects to support the UAE Government in achieving the vision “We the UAE 2031″ to make the UAE ‘the most secure and safe country in the world’, covering radiation safety and safeguards.
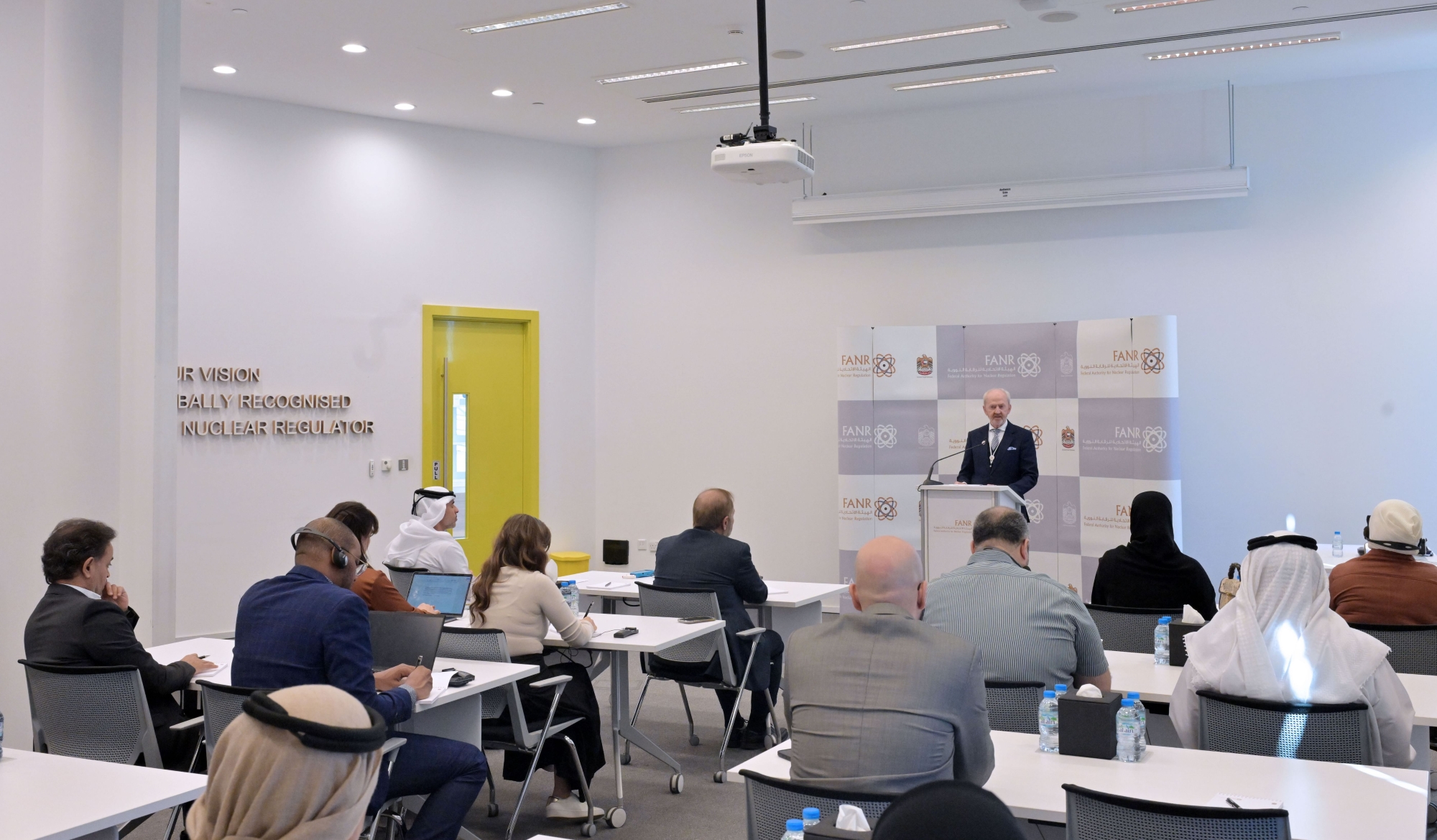
“We plan to expand our international cooperation by exporting the UAE’s expertise to nuclear newcomer countries to learn about the UAE’s journey of building and operating a four-unit nuclear power plant. We will host the 8th International Symposium on the System of the Radiological Protection, to be held in October 2025 in Abu Dhabi where almost 600 experts will discuss recent trends and developments in radiation protection and applications, among other aspects,’’ Christer Viktorsson, Director-General of FANR, told a press briefing in Abu Dhabi today.
“Taking into consideration the nuclear landscape developments, the COP28 pledge to triple nuclear energy by 2050 and the introduction of new technologies such as SMR and AI, we will develop strategies strengthen the regulatory framework which will support the UAE’s economy and carry out our mission to protect the public, workers and the environment,” he said.
Speaking about some of key milestones in 2024 and areas of focus during 2025, Viktorsson said FANR will contribute to the UAE vision to ensure the safe and secure operation of Barakah Nuclear Power Plant and regulate the sector in the UAE by developing and implementing its robust regulatory framework and systems which will further advance this industry.
“As part of our efforts to innovate in our nuclear regulatory activities, we aim to launch this year the FANR Artificial Intelligence Strategy, which will focus on harnessing state-of-the-art technologies into the nuclear sector. We appointed last year Chief Artificial Intelligence Officer, who is working with national and international partners to develop the strategy and support the sector. We aim to join the Trilateral Principles Paper on the Deployment of Artificial Intelligence in Nuclear Activities signed with the USA, Canada and UK.”
During the upcoming World Government Summit, he stated, FANR will join a High-Level Roundtable on The Potential of Artificial Intelligence to Accelerate Small Modular Reactors, which will be organised by FANR, the UAE’s Ministry of Artificial Intelligence and the Nuclear Energy Agency and to be attended by 20 high level national and international nuclear officials.
“In September 2024, the UAE achieved a historic milestone when the Unit 4 of Barakah Nuclear Power plant entered commercial operations; hence, joining the previous three units in delivering electricity around-the-clock to the national grid and contributing to meeting the UAE’s energy needs. FANR continued its robust oversight of the nuclear power plant by conducting 47 safety inspections in the areas of refueling, outage, Power Ascension Test and others. With the four units commercially operational, the UAE has become a successful role model for nuclear newcomer countries, who have shown interest to learn from FANR about its journey and experience from construction to operations.’’
FANR, he added, certified 267 Reactor Operators (ROs) and Senior Reactor Operators (SROs) at Barakah Nuclear Power Plant, as per our licensing requirements, to ensure their readiness and competency in operating the nuclear power plant.
According to Viktorsson, FANR continues to carry out its mission as stipulated by the UAE’s nuclear law that mandates it to regulate the nation’s nuclear sector for peaceful purposes. In 2024, FANR carried out 50 safeguards-related inspections, as well as 96 import and export control inspections, to ensure the licensees’ compliance with FANR’s regulations.
“FANR continues its mission to regulate radioactive sources, physical protection of nuclear material & nuclear facilities. In 2024, 58 security regulatory inspections conducted for licensee facilities using radioactive material and carried out 195 inspections for radioactive source transport vehicles. FANR conducted seven security-related inspections at Barakah Nuclear Power Plant to review all arrangement and implementation to ensure they are in compliance with regulatory requirements,” he further added.
Meanwhile, FANR continued its regulatory mission by licensing and inspecting facilities that are using radiation sources, carrying out 210 inspections in medical and non-medical facilities. It also issued a total of 1,090 licenses for facilities and over 1600 import and export permits.
In addition, FANR’s Secondary Standards Dosimetry Laboratory which is responsible for providing calibration services for radiation measurement equipment , carried out over 1,120 calibrations to customers from the UAE and abroad.
FANR, he said, continued its efforts to boost its research and development capability as well as initiated safety-related R&D work with other partners. In 2024, FANR Board of Management approved its updated Research and Development Policy, which supports the development of regulatory infrastructure and operational capabilities. In 2024, FANR was engaged in 15 research collaboration agreements with many countries covering reactor materials, waste management, and radiation safety infrastructure, among others.
In addition, FANR continued its emergency preparedness activities by conducting and taking part in 18 nationally and internationally drills, including response efforts to trans-national nuclear emergencies as well as organizing 13 training workshops through its Emergency Operations Centre. Our emergency preparedness activities also included a joint exercise with our counterpart the Saudi Nuclear and Radiological Regulatory Commission to assess and evaluate the effectiveness of emergency response systems between the two countries.
Demonstrating its robust capabilities, the UAE joined 43 countries under the IAEA’s Response and Assistance Network, where it expresses readiness to provide international assistance to countries during a nuclear or radiological emergency.
![]() Follow Emirates 24|7 on Google News.
Follow Emirates 24|7 on Google News.